MIST
Magnetosphere, Ionosphere and Solar-Terrestrial
The closest-to-the-Sun-ever direct observation of a shock wave and its heliospheric journey
By Domenico Trotta (Imperial College London)
Shock waves, i.e., abrupt transitions between supersonic and subsonic flows, are present in a large variety of astrophysical systems, and are pivotal for efficient energy conversion and particle acceleration in our universe [1]. Despite decades of research, the mechanisms by which particles are accelerated at shocks are a matter of debate, and are crucial to several applications, ranging from explaining acceleration of cosmic rays to the highest energies [2] to the study of space weather phenomena [3].
Shocks in the heliosphere are unique, being directly accessible by spacecraft exploration, thus providing the missing link to the remote observations of astrophysical systems. Interplanetary (IP) shocks are generated because of solar activity phenomena, such as Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and play an important role in the energetics of the heliosphere where they propagate [4].
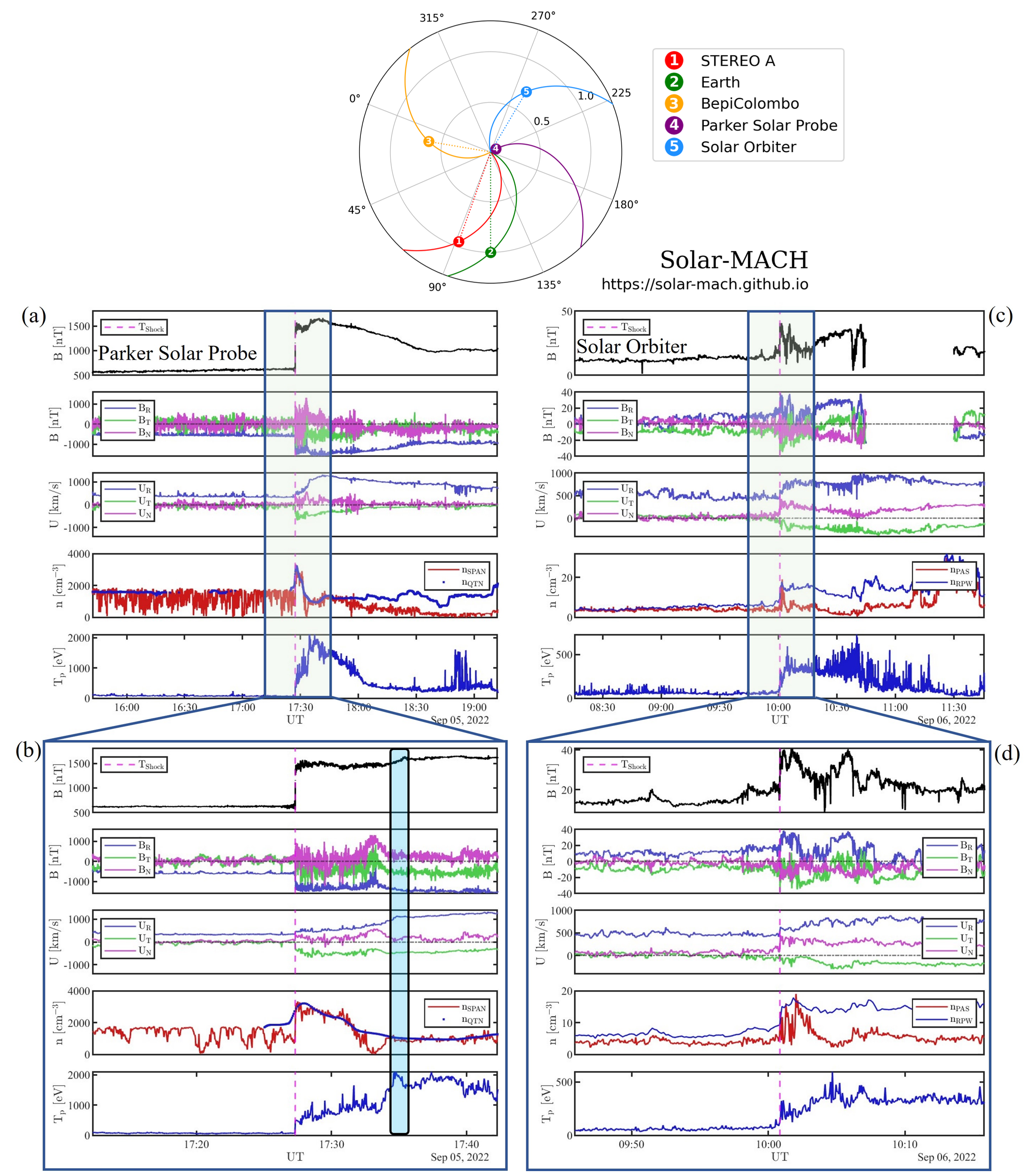
The ground-breaking NASA Parker Solar Probe (PSP, [5]) and ESA Solar Orbiter [6] missions are probing the previously unexplored inner heliosphere, providing datasets with unprecedented resolutions.
We used such novel observational window to report direct PSP observations of a CME-driven shock as close to the Sun as 0.07 A, making it the closest to the Sun direct observation of a shock wave to date. The shock then reached Solar Orbiter at 0.7 AU, enabling us to study the evolution of the shock throughout its propagation in the heliosphere.
We characterized the shock and its environment. At PSP, we found a sharp shock with moderate strength, and investigated how switchbacks, fundamental constituents of the near-Sun environment, are processed by the shock crossing. In contrast, the Solar Orbiter observations revealed a very structured shock transition, with shock-accelerated protons with energies of up to 2 MeV. The differences between the two shocks are due to both evolution effects and the large-scale geometry of the event, crossed by the spacecraft in two points only. This study elucidates how the local features of IP shocks and their environments can be very different as they propagate through the heliosphere.
See full publication for further information:
Trotta et al., ApJ, 962, 2 (2024), DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad187d
References:
[1] Bykov et al., SSRv, 2015, 14 (2019)
[2] Amato&Blasi, Adv. Sp. Res., 62, 10 (2018)
[3] Klein&Dalla, SSRv, 212, 1107 (2017)
[4] Reames et al., ApJ, 483, 512 (1997)
[5] Fox et al., SSRv, 204, 7 (2016)
[6] Muller et al., A&A, 642, A1 (2020)
