MIST
Magnetosphere, Ionosphere and Solar-Terrestrial
Resolving velocity distribution function parameters from observations with significant Poisson statistical uncertainty
By Georgios Nicolaou (Mullard Space Science Laboratory, UCL)
The interpretation of plasma in-situ measurements often involves the application of standard analysis methods to the observations. Some of these methods adopt simplifications that lead to erroneous results. A recently published study led by Georgios Nicolaou uses simulations of plasma measurements and evaluates the statistical errors of plasma parameters determined by applying three different analysis methods to the data. The study shows that two classic fitting techniques that use chi-squared minimization result in significant systematic misestimations of the plasma parameters when applied to samples with credible statistical uncertainty. On the other hand, the application of the Poisson maximum likelihood method to the same data samples always returns the plasma parameters with negligible systematic errors. The authors quantify the expected errors of the examined methods as functions of the statistical significance of the observations. A follow-up study led by Georgios shows that a classic chi-squared minimization method creates artificial correlations to the determined plasma densities and temperatures, which may be misinterpreted as an actual characteristic behaviour of the examined plasma. However, this is not an issue when the Poisson maximum likelihood method is used to analyse the same observations.
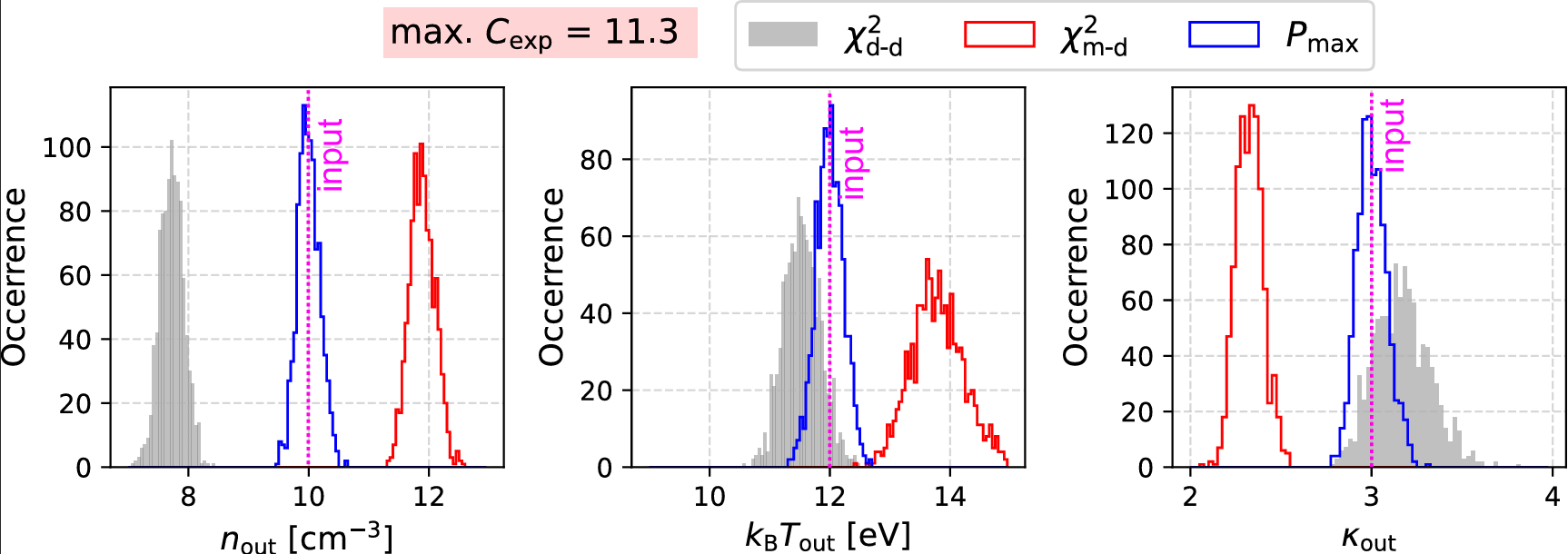
Histograms of plasma bulk parameters determined by applying the three different fit methods to the same measurement samples.
(Left) Plasma density, (middle) temperature, and (right) kappa index, determined by using
Method A: chi-squared minimization with data-driven uncertainty (grey),
Method B: chi-squared minimization with model-driven uncertainty (red), and
Method C: maximum-likelihood method (blue).
The actual plasma parameters (simulation input) are indicated by the vertical magenta line in each panel.
Publications:
Nicolaou, G., Livadiotis, G., Sarlis, N., Ioannou, C. Resolving velocity distribution function parameters from observations with significant Poisson statistical uncertainty, RAS Techniques and Instruments, 2024 3, 874, https://doi.org/10.1093/rasti/rzae059
Nicolaou, G., Livadiotis, G., Ioannou, C. Artificial Polytropic Behavior of Plasmas Determined from the Application of Chi-squared Minimization Analysis to Data with Significant Statistical Uncertainty, The Astrophysical Journal, 2024, 977, 168, 10.3847/1538-4357/ad8f35
